Fundamentals of Intrauterine Insemination
Life is like riding a bicycle, To keep your balance, you must keep moving
Introduction-
Intrauterine insemination( IUI) is an assisted conception technique that involves the deposition of a processed semen sample( Autologous or donor) , in the uterine cavity, overcoming natural barriers to sperm ascent in the female reproductive tract. The rational behind IUI is, to increase the sperm density at the site of fertilization . The first case of human IUI was reported by Guttmacher in 1943. since then, this technique has evolved through various innovation. It is coast effective and non invasive technique, often used for infertility treatment in selected patients with functionally normal tubes.
Pre-requisites of IUI:-
1. At least one functioning tube
2. Total mobile sperm count (TMSC)>10 million (relative)
3. Adequate ovarian reserve
Indications for IUI:-
A complete couple workup that includes- patient history, physical examination, clinical and laboratory investigations, is mandatory to justify to choice in favour of IUI and guide alternative patient management.
1. Unexplained infertility
2. Mild to moderate male factor
3. Minimal to mild endometriosis
4 Unlateral tubel disease
5. Cervical factor : Less readily diagnosed, as post coital test is not routinely performed nowadays.
6. Sexual dysfunction
a. HypospadiasICSI
b. Retrograde ejaculation
c. Erectyle dysfunction
d. Vaginismus
Indications for Donor IUI:-
1. Non- obstructive Azoospermia
2. Obstructive Azoospermia, when In-vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic sperm Injection (ICSI) is not affordable.
3. Severe Oligo- Astheno- Terato-Zoospermia (OAT) when IVF for ICSI is not affordable.
4. Recurrent IVF/ ICSI failure.
5. Inheritable genertic disease in male
6. Single woman/ Lesbian couples
Contraindications of IUI:-
1. Active pelvic infection, cervicitis
2. Severe endometriosis
3. Severe male factor infertility
4. Poor ovarian reserve, where IVF is preferable.
When should IUI be initiated in Infertile couples ?
In couples who have reasonable chance of becoming pregnent through normal intercourse ( Hanualt score 30-40%) , expectant management for at least 6 months should be the first option, because, in these good prognosis couples, ovarian stimulation with IUI, does not improve live birth rates significantly.
In couples with unexplained infertility, and a Hanualt score below 30%, IUI with ovarian stimulation should be initiated, as it results in significantly higher cumulative live birth rates, compared to expectant management.
Hunault score is a prognostic index score that takes into consideration – woman’s age, type and duration of infertility , sperm progressive mobility and patients referral status, to assess the chance of natural conception for the infertile couple.
Natural Cycle IUI:-
Natural cycle IUI may be done in case of moderate male factor infertility ( TMSC <10 million/ml) , where studies have shown that addition of ovarian stimulation, does not increase the pregnency rate. This is an contrast to mild male factor infertility ( TMSC > 10 million/ml) , where addition of ovarian stimulation, significantly increase the pregnancy reate to natural IUI.
IUI in natural cycle in case of unexplained infertility , does not improve the pregnancy rate signicantly, and hence, IUI should be combined with ovarian stimulation in the these cases.
Ovarian Stimulation Protocols IUI
Though the main utility of ovulation inducing drugs is in oligo-or an an-ovulatory patients , IUI is almost always combined with ovarian stimulation(OS). The rational of ovarian stimulation is to cause multi follicular development, which increase the chance of pregnancy. In meta- analysis , the chance pregnancy was 5% higher with two follicles, and 8% higher with three or four follicles.
The commonly used drugs are:-
1. Clomiphene citrate
2. Aromatase Inhibitor
3. Gonadotropins
Clomiphene Citrate(CC):- It is a selective estrogen receptor modulator(SERM). The usual starting dose is, 50-100 mg per day , for 5 days starting from day 2-6 of mense. The dose can be increased by 50 mg in successive months, till ovulation is documented. Though the maximum dose is 250 mg/day , the pregnancy rate does not increased at dose above 150mg, as the inhibitory effect of CC on estrogen receptors in endometrium, and cervical mucus becomes more pronounced. The advantage of CC are – ease administration , affordability, no need for strict monitoring, no cold storage required , and less chances of multiple pregnancy.
patients who fail to ovulate with the maximum dose of CC (150mg) for 3 cycles, are clomiphene resistant and can be treated with gonadotropins, aromatase inhibitor or a combination of CC and gonadotropins.
patients who fail to conceive despite successful ovulation for 6 cycles with CC , are considered to have clomiphene failure , and should be evaluated for other cause if infertility . Combined and alternative strategies may be tried. Eventually, Assisted Reproductive technology needs to be done for those fail to conceive despite 12 successful ovulatory cycles , in the absence of other cause.
Aromatase Inhibitor(AI):- Letrozaole is a third generation, class II – AI , which is useful in patients who fail to respond to CC, either due to CC resistance or thin endometrium . The dose is 2.5 to 5 mg daily, for 5b days from 2-6 of menses. AI inhibits the conversion of androgen to estrogen, leading to low circulating levels of estrogen. As a result , the hypothalamus and pituitary are released from the inhibitory feedback of estrogen, leading to increased release of gonadotropins, and hence folliculogenesis. Letrozole has less chance of multiple pregnancy and does not adversely effect the endometrial thickness unlike CC. The success rate is comparable between AI and CC.
Gonadotropins:- The use of human menopausal gonadotropins of purified follicular stimulating hormone in male, and unexplained infertility , is associated with higher pregnancy rate compared to CC. However, this comes with the increased risk of multiple pregnancies, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, increased coast treatement , and a need for more frequent monitoring. Despite the higher pregnancy , the birth rate with gonadotropins used in IUI , is similar compared to CC. The pregnancy rate similar irrespective of type of gonadotropin used.
CC/Letrozole+gonadotropin combined therapy:- This therapy used in CC failure cases. CC is given at a dose of 100mg daily( or Letrozole 5 mg daily) from day 2 to day 6 of menses, and hMG or FSH ( 75 or 150 IU) is given on day 7 and 8 . Transvaginal ultrasound is commenced from day 9, and further doses of gonadotropin are given , if required . The advantage of this combined therapy are- higher success rate than CC alone, low treatment cost with less complication , compared to gonadotropin therapy.
While choosing the stimulation protocol in IUI, the success and complication rates, response to previous treatment , and patients affordability should be considered. The protocol should be individualized on a case to case basis.
Timing of Ovulation Trigger and IUI:-
Ovulation is triggered when the leading follicle reaches 18mm in size. In a natural cycle , the ovulation occurs after a mean of 32(24-56) hours after the onset of L.H surge, and the released ovum is fertilizable uo to 12-24 hours, after its released. Washed sperms in the processed semen can fertilize oocyte only within the next 2-3 hours, because removal of seminal plasma initiates sperm capacitation by changes in the acrosome. Therefore, best time for insemination to maximize the chances of fertilization is within 2-3 hours of semen preparation.
In a natural cycle, IUI should be done 1 day after detection pf spontaneously detected LH surge. Following hCG injection , ovulation starts after 32-38 hours, hence IUI should be done at 36-38 hours.
The commonly used drugs for triggering ovulation are- urinary hCG ( 5000 or 10000 IU intramuscularly) and recombinant hCG ( 250 mcg subcutaneously) .Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or recombinant LH are less commonly used . According to a cochrance systematic review, there is no difference in live birth rate between hCG trigger or LH surge in natural cycle, urinary or recombinant hCG and hCG or GnRH agonist. Latest evidence suggests that, there is no significant difference in clinical pregnancy or live birth rates, when IUI is done between various time frames that range from 24 to 40 hours.
Semen Quality and preparation :-
The main limitation in comparing IUI outcomes in relation to varying semen parameters is the lack of validate definition and strict cut-off values to differentiate between mild, moderate, and severe male fertility. Best result is seen when , TMSC is > 10milion/ml( mild male factor) . evidance suggests that , TMSC > 1 million/ml and morphology .4% is the cut-off below which , IUI should be withheld.
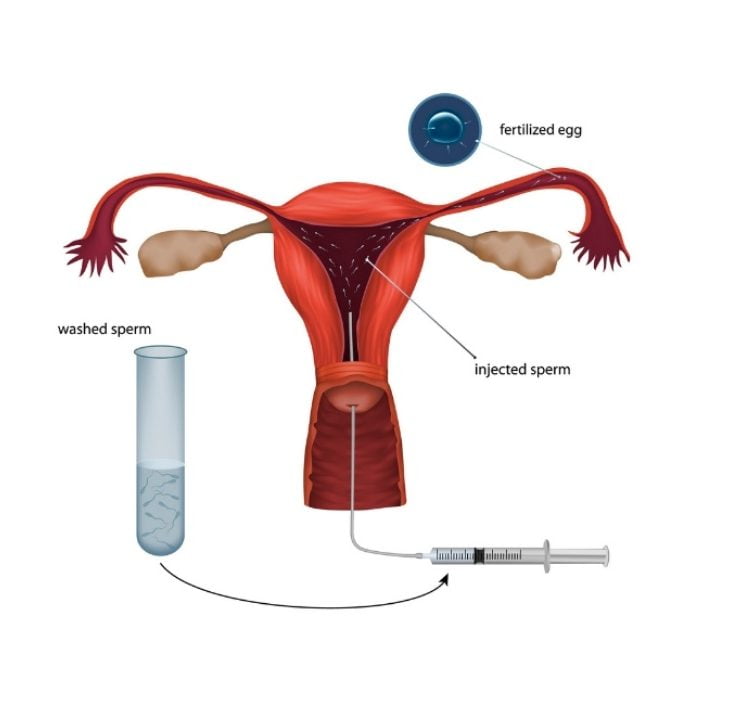
Semen collection for IUI should preferably done at the clinic in non toxic , disposal and sterile wide mouth containers. The semen can also be collected at home after a natural intercourse, directly into the containers , and should be brought to the laboratory within 20 minute. Regular condoms should not be used for collection, as the lubricant used may be spermicidal. Special non toxic condoms are available for collection. The semen parameters are then checked and processed. The aim of semen processing is to separate sperm from seminal plasma , as prolonged exposure to seminal plasma result in a marked decline in both motility and viability . Hence , semen processing should be done within 30 minutes of ejaculaton. IUI should be done best result in terms of clinical pregnancy, as further delay leads to decrease in number of fertilizable motile sperm.
The most common methods of semen prepartion are- swim up and density gradient technique. A recent study compared these two technique with respect of their effect on semen parameters. It was found that in the density gradient method, there was significantly higher increase in the DNA fragmentation rate in the viable sperm , between the pre and post wash semen , compared to the swim up technique. Implying that swim up technique should be used to select spermatoza in assisted reproductive technique(ART) when possible.
Technique of IUI:-
* Verication of the semen sample and patients name
*Assesment of count and motility of the processed sample
* Partially fillid urinary bladder.
*No antiseptic solution to be used for cleaning
*Clean the cervix with saline swab .
* Cervical mucus aspiration before IUI
* Use sims or self retaning speculam.
* IUI catheter should be introduced as atraumatically as possible . Once past the internal cervical the catheter is advanced to depth of at least 4 cm , but no more than 6 cm to avoid trauma to the endometrium.
* In case of difficulty in negotiating the internal cervical, cervix can be held with tenaculum or vulselum and gently pulled to straighten and align the cervical and uterine canal, to facilitate the passage of the catheter. Once the catheter is inside the uterine cavity, the tenaculam is released so that the uterus goes back to its original position before the semen is injected.
* Slowly inject 0.3 to 0.5 ml of processed semen over 1 minute.
* Air gap to be kept in the syrings between the semen and plunger of the syringe so that all processed semen can be pushed inside the cavity.
*Allow rest for at least 15 min.
Rest after IUI:-